Drainage System India









Drainage System India
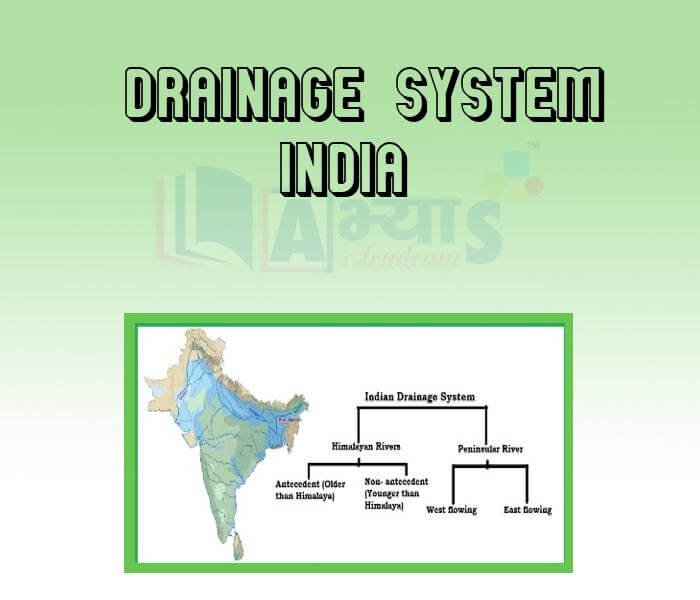
DRAINAGE SYSTEMS IN INDIA
The drainage systems of India are mainly controlled by the broad relief features of the sub-continent. The rivers of India are broadly classified into two major groups
Apart from originating from two major physiographic regions of India, the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers are different from each other in many ways.
The Himalayan Rivers: Most of the Himalayan rivers are perennial, which means that they have water throughout the year. These rivers receive water from rain as well as from melted snow from the high mountains. The Indus and the Brahmaputra originate from North of the mountain ranges. They have cut through the mountains, making gorges. The Himalayan rivers have long courses from their source to the sea. These rivers perform intensive erosion activity in their upper course and carry huge loads of silt and sand. These rivers form meanders, Ox-bow Lakes and other depositional features during their middle and lower courses in the floodplains. These rivers have well developed deltas.The Peninsular Rivers: These are seasonal rivers as their flow is depend rainfall. During the dry season, the large rivers even the flow of water in their channel. Himalayan. The Peninsular rivers have shorter and shallower courses compared to their Himalayan counterparts Peninsular rivers originate in the Western Ghats towards the Bay of Bengal.Some Features Made by Rivers• Gorges: Deep narrow passages with steep rocky sides through which rivers may flow.• Ox-bow Lake: A crescent-shaped lake formed when a meander of a river or stream is cut off from the main channel.• Deltas: Triangular shaped alluvial deposits at the mouth of rivers where they enter the sea.
Below the ocean bed there are troughs and basins which are known as ____________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.
